Netstat (Network Statistics)
Netstat (Network Statistics) is a Command Prompt command that launches NETSTAT.EXE, a TCP/IP utility found in the Windows operating system. Netstat displays all kinds of data related to network connections. In order to obtain some specific data, you can use Switches along with the netstat command in Command Prompt. These Switches can be used either one at a time, or in a combination with other switches to get desired information in one go.
Syntax: netstat –switchname(s)
One of the benefits of using Netstat is its ability to identify which programs are connected to the Internet, and transferring data. You can identify such programs by using the –b switch with the netstat command.
How to Detect Malware (Viruses) Using Netstat in Windows
Step 1: Press Windows + X keys together to open the Windows Super User Menu. Click on the Command Prompt (Admin) option to open Command Prompt with Administrative privileges.
Step 2: In the Command Prompt window, type netstat followed by a switch name. In this example, we’ll use –b. Press the Enter key. The switch –b displays the executable involved in creating each connection or listening port.
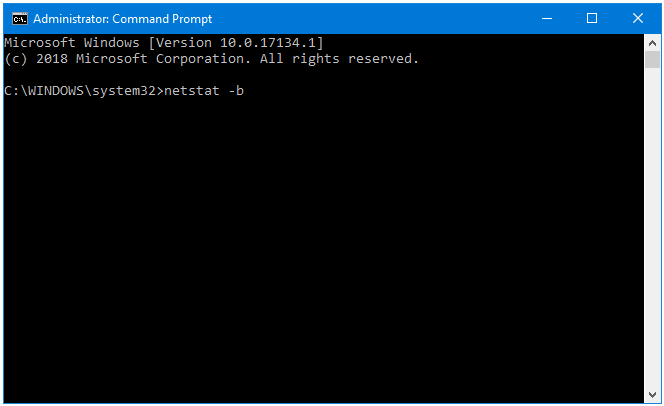
Step 3: The netstat command displays the Active Connections on your system.
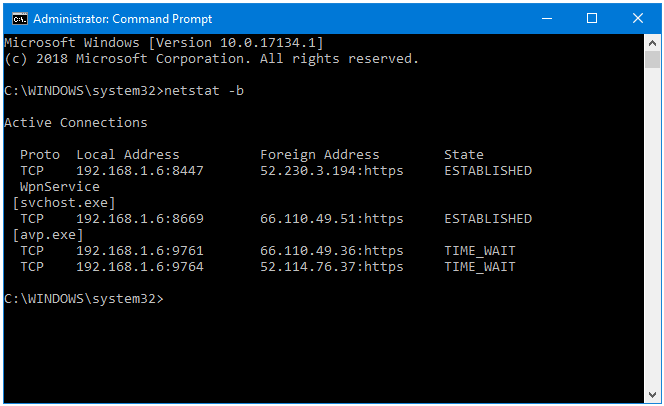
The data is presented in four columns – Proto, Local Address, Foreign Address, and Status.
Proto – Displays the Network Connection Protocol.
Local Address – Displays the Address of the User’s Computer.
Foreign Address – Displays the Address of the IP Address the User’s Computer is Connected to.
Status – Displays the Current Status of the Network Connection.
There are two processes with ESTABLISHED connection here:
- WpnService
- exe
Let’s find out about them.
In order to find more information about the processes that are connected to the Internet, we need to get their PID (Process Identifier). To display the PID along with the information that we currently have, we will rerun the netstat command, but this time using a combination of two strings – b and o. The switch –o displays the PID (Process Identifier) associated with each network connection.
Step 4: In the Command Prompt window, type netstat –bo, and then press Enter.
Step 5: Now, we have a fifth column called PID as well.
Step 6: Right-click on the Taskbar, and click Task Manager.
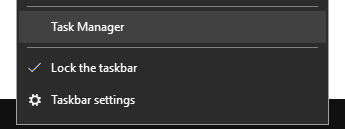
Step 7: The PID column is hidden by default in the Windows Task Manager. Right-click on the Information bar, and click on PID to show it as a column in Task Manager.
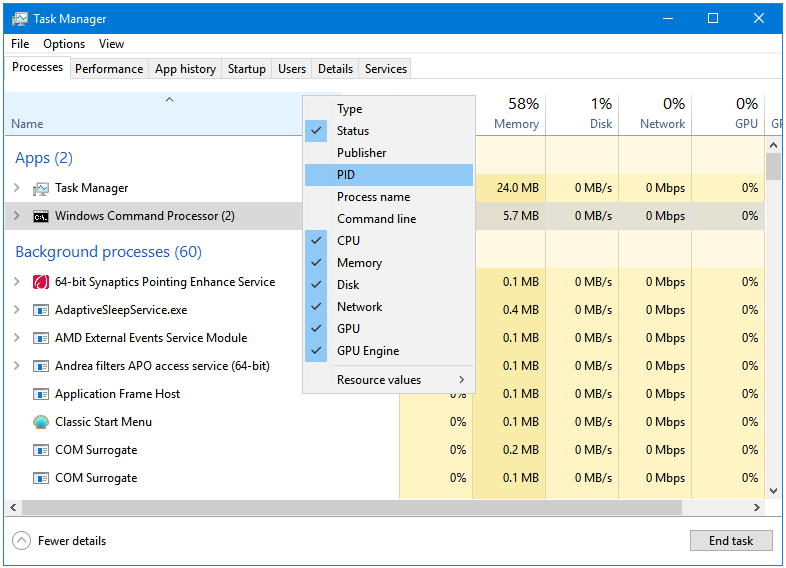
Step 8: Sort the processes by PID.
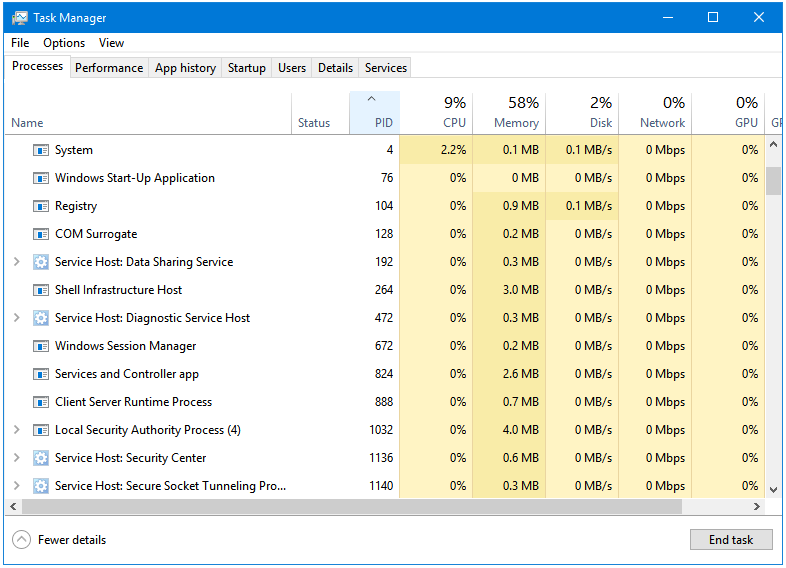
Step 9: Now, here you can easily locate the process through its PID.
The WpnService process is Service Host: Windows Push Notifications.
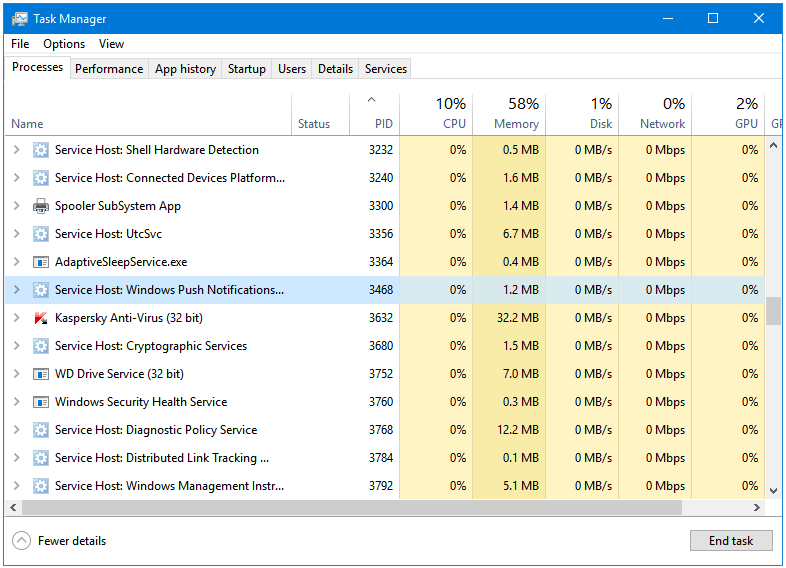
The avp.exe process is Kaspersky Anti-Virus.
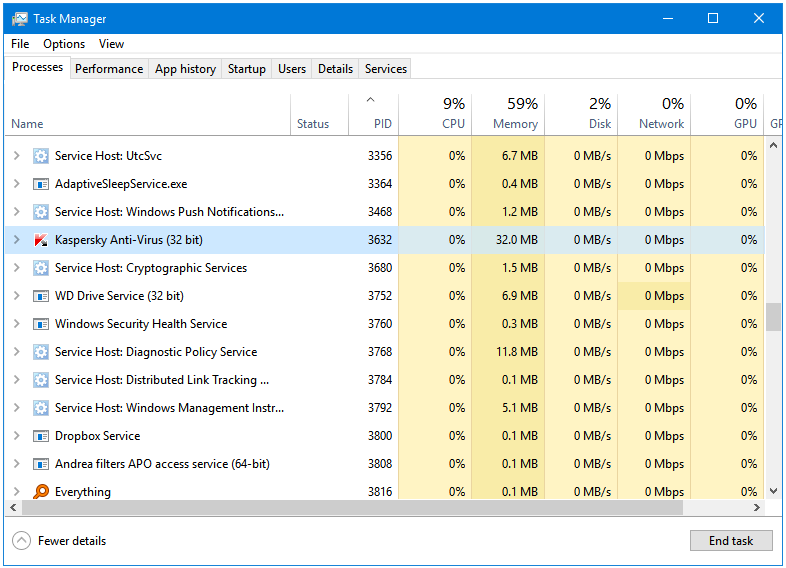
So, you can see how we can find out about the processes that are currently connected to the internet. If you see a program name that does not look like a familiar, you can easily track and, and block or remove it.
This way, we can detect and block malware (viruses) using the netstat command in Windows.
Thanks for this article but I still don’t know how to identify a program or process that should not be there.
Hi Rob,
Thanks for commenting. This is just another method to find all those programs that are connecting to the Internet. Some type of Malware stay on the computer, and send the confidential information such as keystrokes in the background. Using this method, we can identify the programs that are active on our computer, and sending data from our computer to a server. If all of the programs are known ones, then there is nothing to worry about.
Like I said, this is just another method. The first one should be running regular scans with your Antivirus. Having an up-to-date Antivirus and Firewall on our PC takes care of most kind of malware.
This is helpful. I used to remember how to do this stuff. What else can you tell me, I would like to ensure I can use my laptop properly.
Thank you for the comment. Please go through the Categories section in the Sidebar to find content about various topics.